Policy Information
| Policy Number: 2.01 | Effective Date: 09/16/2012 |
| Responsible Unit: Financial Management | Last Revised Date: 07/16/2024 |
| Email: FNSV-Financial-Management@arizona.edu | Phone: 520-621-9097 |
Purpose and Summary
The purpose of this policy is to describe the structure of the University’s accounting system. Proper structure allows for accurate accumulation of transactional data, which is required for financial management and reporting.
Source
Governmental Accounting Standards Board, including but not limited to Statement 54
National Association of College and University Business Officers, Financial Accounting and Reporting Manual for Higher Education (FARM), including but not limited to ¶300 and ¶700
Scope
This policy applies to all University locations and units, including all University extensions, satellite locations, and off-site campus units, both domestic and international.
Definitions
- Account: An individual pot of money that is established for a specific purpose, with primary responsibility for its activity assigned by Account Roles. The Accounts in UAccess Financials are 7-digit numbers that are approved by Financial Services. Similar types of Accounts will all be in the same range of numbers. See Table 1 below.
- Attributes: Non-dollar, descriptive data attached to the Account. These Attributes often determine how the Account can be used in a transaction and are used to identify financial information for reporting purposes or drive specific processes.
- Chart of Accounts (CoA): The structure through which financial transaction data is organized and reported. The CoA serves as the common language for financial transactions, organizes and segregates expenditures, revenues, assets, and liabilities, and supports financial and management reporting.
- Fund Group: A self-balancing grouping of Accounts that represents specific activities, objectives, restrictions, or regulations. Fund Groups have an intended use or purpose and may have spending restrictions imposed by donors, sponsors, federal or state requirements, or the University.
- State Funds: These funds primarily consist of tuition and fee revenue collections and State General Fund appropriations. State funds are used to support the academic programs and the general operating expenses of the University. A State General Fund appropriation may specify the general purpose or purposes for which the appropriation may be used. Any changes to these allocations must go through a legislative process. Tuition and fee revenue collections allocations are governed by the Arizona Board of Regents and changes in the intended use of the funds can be made by them without having to go through a legislative process. ABOR may delegate authority to make changes in the intended use of these funds to administrative units within the University.
- Designated Funds: Funds that have been limited for a specific purpose by specific action of the Arizona Board of Regents or by an administrative unit of the University authorized by ABOR to designate funds. Designated funds account for the activities of indirect cost recoveries, conferences, and certain instructional activities, such as summer session, continuing education, international programs, and extension programs. Also included are funds received from the sale of products or services that are not more appropriately classified as Auxiliary Enterprises. For example, sales of by-products of instructional, research, or public service activities, such as the sale of produce by the College of Agriculture, Life & Environmental Sciences, or the sale of hearing aids by the Speech and Hearing Science Department, are accounted for as Designated funds.
- Auxiliary Funds: Funds generated by revenue from an established auxiliary enterprise. An auxiliary enterprise is a separately organized University unit or activity that exists predominantly to sell products or services to students, faculty, or staff on a continuing basis and is managed essentially as a self-supporting business. The auxiliary enterprises generally support the instructional, research, or public service activities of the University. An auxiliary enterprise charges fees directly related to, although not necessarily equal to, the cost of the products or services. The general public may be served incidentally by some auxiliary enterprises. Sales of by-products of instructional, research, or public service activities are not classified as Auxiliary funds; see the definition above for Designated funds. Examples of auxiliary enterprises include Housing & Residential Life, Intercollegiate Athletics, Bookstore and Campus Recreation.
- Sponsored Projects Funds: Restricted funds received from Federal, State, or other governmental agencies or private organizations that are provided on a contractual or grant basis with the restriction that the funds be used for a specific purpose. These funds may only be used for the intended purpose and must be spent in accordance with terms specified in an agreement established between the sponsor and the University. If not, the funds may revert to the sponsor.
- Other Restricted Funds: Funds received from outside sources with specific restrictions on how the monies are to be spent that are not more appropriately classified as Sponsored Projects. Included are restricted gifts, governmental grants for student aid, and private grants and scholarships.
- Technology and Research Initiative Fund: Funds established by Arizona law that provide sales tax revenue to ABOR to administer for the purposes of expansion of research, workforce development, and increasing access to public higher education. Initiatives include Space Exploration & Optical Sciences; National Security Systems; Improving Health; Water, Environmental, & Energy Solutions; and Higher Education Access for Workforce Development.
- Loan Funds: Resources available to the University for loans to students for financing of their education and the balance of existing loans outstanding. Loan funds may originate from restricted sources, such as gifts, endowment income restricted to loans, and refundable grants matched with institutional funds. The Arizona Board of Regents or authorized University administrators may designate or transfer unrestricted funds to Loan Funds. Funds for loans may be specified for use in the National Direct Student Loan/Perkins program, temporary and long-term loan programs, or the health-related professions loan programs.
- Endowment Funds: A special fund whereby the principal is held for investment and the interest earned on the principal is spent as directed by the donor. For more detail on endowments, see policy 8.13 Endowments in the Financial Services Manual.
- Plant Funds: Unexpended plant funds, renewal and replacement funds, debt service funds, and investment in plant funds.
- Unexpended Plant Funds: Resources and any associated indebtedness to be used for the acquisition of physical properties for institutional purposes, which have not yet been expended. Indebtedness incurred to finance plant acquisition and construction is included as a liability of the unexpended plant funds until the proceeds of the indebtedness are expended. Examples of restricted unexpended plant funds include proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt and gifts designated for capital projects. Unrestricted unexpended plant funds include State capital or building renewal appropriations, as well as funds set aside by the University from unrestricted fund balances.
- Renewal and Replacement Funds: Resources accumulated for renewal and replacement of the capital facilities of the University.
- Debt Service Funds: Resources for the payment of debt service charges and the retirement of long-term indebtedness. Examples of debt service funds include those for bonded indebtedness, certificates of participation, lease purchase agreements, and other forms of long-term indebtedness.
- Investment in Plant Funds: Records the net capital acquisitions of the University. Capital assets are classified as land, buildings and improvements, infrastructure, equipment, library acquisitions, and construction in progress. The principal balance of liabilities incurred to acquire capital assets is recorded in this fund.
- Agency Funds: Resources held by the University as custodian or fiscal agent for an organization or entity (the Agency) external to the University. The University must act with reasonable care in administering the funds of others. Agency accounts do not carry a fund balance that belongs to the University. Transactions of Agency funds are not included in the revenues or expenses of the University for financial reporting purposes.
- Functional Expense Classification: A method of grouping expenses according to the purpose for which the costs are incurred. The classifications tell why an expense was incurred rather than what was purchased. Reporting expenses by functional classification helps donors, granting agencies, creditors, and other readers of the financial statements to understand the various mission-related activities of the institution and their relative importance. The University follows the NACUBO Functional Expense Definitions.
- Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB): The independent, private sector organization that establishes accounting and financial reporting standards for U.S. state and local governments that follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
- National Association of College and University Business Officers (NACUBO): A membership organization that represents college and university professionals and other stakeholders who work in higher education business and finance. NACUBO publishes the Financial Accounting and Reporting Manual for Higher Education, guidelines, and advisory reports to assist business officers and their auditors with complex and changing financial accounting requirements specific to higher education.
- Object Code: A four-digit number that captures the nature of a transaction and tells what was purchased. Object Codes categorize revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and net assets activity within an Account. See Table 2 below.
- Sub-Fund Group: Identifies a more detailed activity, use/purpose, objective, or spending restriction on an Account and rolls up to a Fund Group.
Policy
- UAccess Financials is the official accounting system used at the University.
- The accounting system and Chart of Accounts will be structured to maintain records of each source and use of funds and to record and accumulate financial activities in compliance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and standards established by the GASB.
- Accounting information will be maintained to comply with applicable accounting and reporting requirements under Federal law, State Statute, and Arizona Board of Regents (ABOR) policies, and as required under the terms of specific agreements with external entities and administrative policies of the University.
Procedures
- Accounts are established in the system to enable the University and administrators to monitor and report on the activity of various sources of funds.
- Fund Groups and Sub-Fund Groups, which are Attributes, are used to group Accounts with like activities, objectives, restrictions, or regulations.
- The Account Attribute, AICPA Function Code, is used to distinguish expenses by Functional Expense Classification. Refer to Account NACUBO Functional Expense Definitions.
- Once an Account has been established in the UAccess Financials system, transactions may be posted to the Account.
- Transactions are posted directly into the system through UAccess Financials Electronic Documents (eDocs) or may be posted to a subsystem that will subsequently be fed to UAccess Financials in a batch feed. For additional information on the use of common UAccess Financial eDocs, see the Most Common Document Types chart.
- Accounts and Object Codes are required to be entered when transactional dollar information is recorded in the system. See Table 1 and Table 2 below.
- Each type of Object Code has a normal balance of either debit or credit. See Table 2 below. In Financials, eDocs use the words “To” and “From” to represent debits and credits. See Table 3 below.
- Additional optional CoA segments can be entered on a transaction, such as Project Code, Sub-Account, and Sub-Object Code. Refer to Chart of Accounts – Definitions and Examples for additional information.
- UAccess Financials is a double-entry accounting system. This requires that a document’s debits and credits balance. The system will not allow a document to be submitted if it is out of balance.
- The transactions posted to an Account are accumulated in the system. After nightly batch is run, transactions can be viewed on various reports in UAccess Analytics.
- Refer to policy 6.10 Account Management for responsibilities and guidelines for establishing, modifying, monitoring, and closing UAccess Financials Accounts.
Table 1: Account Structure
| Fund | Account Number |
|---|---|
| State | 1000000 - 1359999 1400000 - 1599999 |
| Auxiliary | 1600000 - 1999999 |
| Designated | 2000000 - 2999999 |
| Sponsored Projects | 3000000 - 4999999 |
| Other Restricted | 1360000 - 1399999 5000000 - 5829999 5860000 - 5999999 |
| Technology and Research Initiative Fund | 5830000 - 5859999 |
| Loans | 6000000 - 6999999 |
| Endowments | 7000000 - 7999999 |
| Plant | 8000000 - 8999999 |
| Agency | 9000000 - 9399999 |
| Audit | 9900000 - 9999999 |
Due to conversion of FRS accounts to UAccess Financials, there will be some Account numbers, established prior to 2011, that do not fall in the correct range. All new Accounts should conform to the correct number range. Additional details on Account number ranges and Sub-Funds can be found in the Fund-SubFund Table.
Table 2: Object Code Structure
| Assignments | Object Code* | Normal balance |
|---|---|---|
| Revenues and Transfers | 0010 - 0999 | Credit |
| Personal Services | 1000 - 1999 | Debit |
| Employee Related Expenses | 2000 - 2999 | Debit |
| Operations/General Expenses | 3000 - 5999 | Debit |
| Travel | 6000 - 6399 | Debit |
| Student Support | 6400 - 6891 | Debit |
| Capital and Transfers | 7000 - 7999 | Debit |
| Assets | 8000 - 8999 | Debit |
| Liabilities | 9000 - 9899 | Credit |
| Fund Balance | 9900 - 9999 | Credit |
*Detailed listings and definitions of object codes are provided within the Accounting Support section of the Financial Services website.
Table 3: Debits and Credits
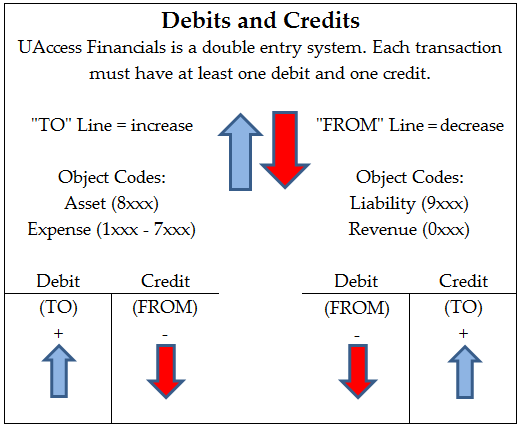
Fund Balance (9900) is only adjusted once a year during balance roll forward. For accurate fund balance, please use UAccess Analytics reports (for example, the Assets, Liabilities and Fund Balance Report found on the General – Financial Management dashboard).
Frequently Asked Questions
- Who should I contact if I am unsure of an Account attribute?
Please contact your Fund Accountant.
Related Information
Policy 6.10 Account Management
Policy 8.13 Endowments
Most Common UAccess Financials Document Types
Chart of Accounts – Definitions and Examples
Account NACUBO Functional Expense Definitions
Account AICPA/HEFC Codes
Object Codes Definitions and Crosswalks
Records Retention Policy
Internal Control
* Please note that sections titled Frequently Asked Questions and Related Information are provided solely for the convenience of users and are not part of the official University policy.
